The Different Types Of Chronic Urticaria
Chronic urticaria is a condition characterized by the appearance of pimples and itching for a period of more than six weeks. Despite efforts to identify them, many of the causes of hives are unknown.

Chronic urticaria is a skin disease characterized by the appearance of skin lesions with different types of presentation. These lesions are usually accompanied by itching, or itching in the affected area. According to various studies, it is estimated that 20% of the world’s population has suffered from it at least once in their lifetime.
Due to its high prevalence and the discomfort of its clinical picture, it is essential to know the causes, the different types as well as the epidemiology of urticaria in order to address it effectively.
Background and frequency of the disease
Before addressing the peculiarities of this disease, it is precisely interesting to know the dynamics of presentation that it follows over time. This is one of the first steps necessary to consider its treatment and containment.
An article from the Buenos Aires Medical Review provides some very interesting data on urticaria:
- It is estimated that 15 to 25% of the world’s population suffers from hives at least once in their lifetime
- The prevalence of chronic urticaria is around 1%: in other words, one in a hundred people in a given population nucleus suffers from it.
- It is isolated in 45% of cases and accompanied by angioedema (swelling of the skin) in the remaining percentage
In addition, it should be noted that there are two distinctions of type of urticaria. It is considered acute when the episode lasts for up to six weeks, and chronic from then on. As incredible as it may seem, its origin and cause are unknown in 80% of cases.
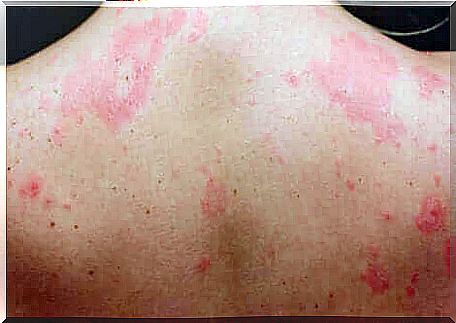
Types of chronic urticaria
Although it appears to be a harmless disease due to its superficial nature, chronic urticaria can dramatically decrease the quality of life of patients. Clinical studies equate the impact of this disease with some cardiac pathologies.
According to the Association of People with Chronic Urticaria, it has diverse origins, mainly related to the following processes:
- Autoimmune reactions
- Intolerance and hypersensitivity to certain drugs
- Infectious process
- Foodborne allergies
There is no official division into categories or types of chronic urticaria, which has been validated by an international medical institution. But we can classify it according to its causal agents. Below are the three most common types.
Chronic hives caused by autoimmune reactions
Dermatological studies highlight that this is the most common cause since it occurs in 45% of cases. The body itself activates the skin cells, which causes them to release histamine (a component involved in the immune system) and produce hives.
However, other medical journal articles claim the general lack of knowledge about this mechanism. Indeed, the reason that activates the mediating antibodies of the immune system is not yet fully understood. About 15% of cases present with diseases associated with the thyroid glands (autoimmune thyroiditis for example).
Chronic urticaria caused by infections
There are infectious processes and viral agents, bacteria and fungi that are able to promote the onset of chronic urticaria. Here are some of them:
- Hepatitis A and B virus
- Streptococcus invasion
- Mycobacterium tuberculosis , a bacterium that causes most cases of tuberculosis worldwide
- The herpes simplex virus
On the other hand, special mention should be made of the case of infection with Helicobacter pylori , a bacterium which lives in the epithelium of the human stomach and which seems to be linked to this pathological process. A study from the journal Allergologia et Immunopathologia reports that 71% of patients with chronic urticaria who participated in the study had this microorganism in their digestive system.
However, only three of the 21 patients followed showed substantial improvement when the bacteria were cleared from their gastrointestinal tract. Therefore, an obvious correlation between these two factors is still questionable.
Urticaria caused by drugs
Various analyzes in the scientific world explore the link between drug consumption and the onset of chronic urticaria. This pathology can be aggravated by the ingestion of a series of drugs, including aspirins and other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
Treatments for the different types of chronic urticaria
A literature review published on the ScienceDirect website in 2015 lists some of the most effective treatments for chronic urticaria. Here are the most relevant:
- First generation antihistamines, such as diphenhydramine
- Acrivastine
- Cetirizine and loratadine, as second generation options, with fewer side effects associated with drowsiness
- Various corticosteroids, some of which have a shorter or longer life. In other words, they stay longer or shorter in the body.
Most of these drugs are aimed at modulating the response of the immune system and reducing the inflammatory process. Depending on the underlying cause of the disease (so difficult to identify), multiple medications may be needed at the same time.
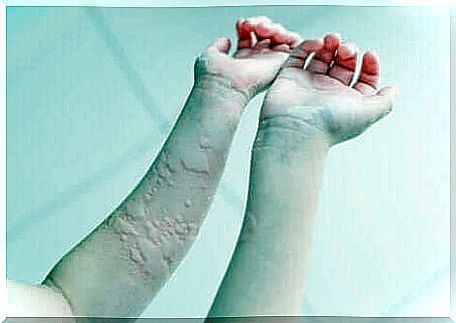
Types of chronic urticaria: what to remember?
As we have seen, chronic urticaria is a multifaceted pathology that is still unknown today. The exact causes and the most effective treatments are still partly a puzzle to the scientific community.
Either way, we know that any rash that lasts longer than six weeks is a clinical manifestation of chronic urticaria. In this case, it is essential to go to the doctor in order to start treatment. Certain general measures will then be necessary to alleviate the bothersome symptoms and, possibly, certain medications will be prescribed.